Semiconductor Ceramic Nozzles :Material Types and Selection Guide
- 2026-01-22 Industry News
A technical guide to ceramic nozzle materials for plasma etching. Learn to select the right Alumina, AlN, or ZrO₂ components to enhance precision, durability, and production yield in microelectronics manufacturing.
Introduction
In semiconductor manufacturing, microelectronics processing, and high-precision industrial spray coating processes, ceramic nozzles are core components that support equipment operational stability and process precision. During the operation of plasma etching equipment, nozzles not only play roles in gas introduction and guidance, flow field uniformity control, and reaction area confinement, but are also required to maintain chemical inertness and mechanical stability over long periods in high-temperature, highly corrosive, vacuum, or low-pressure environments.
As chip manufacturing processes are miniaturized and the requirements for etching precision become even more stringent, the selection of ceramic nozzle materials increasingly affects wafer processing yields, equipment stability, and maintenance costs.
Typical challenges that can occur when ceramic nozzle material selection is inappropriate:
❌ Rapid nozzle wear — Shortened service life
❌ Dimensional drift of orifice diameter — Impact on process precision
❌ Deposition due to chemical reactions — Wafer contamination
❌ Localized overheating — Cracking and breakage
Therefore, correctly understanding the characteristics of various ceramic nozzle materials and their applicability in plasma etching equipment is a vital focus for equipment engineers and process technicians during design and selection.
Comparison of Commonly Used Ceramic Nozzle Materials
1. Alumina (Al₂O₃) Ceramic Nozzles
Alumina (Al₂O₃) is one of the most widely used high-performance ceramic nozzle materials in industrial applications, extensively adopted in semiconductor plasma etching, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), precision spray coating, and other high-temperature/highly corrosive environments. In plasma etching equipment, while subjected to impacts from high-temperature, high-velocity gas flows and the influence of corrosive process gases, alumina can maintain orifice precision and dimensional stability over the long term, contributing to consistent processing and yield. Alumina possesses high hardness and excellent structural stability, making it resistant to wear and deformation even during extended operation. Furthermore, advanced processing technologies allow for the formation of complex shapes and micron-level micro-holes, meeting custom process requirements. Additionally, by compounding with other ceramic materials, impact and thermal resistance can be further enhanced, delivering more stable and reliable performance in advanced industrial applications.
● High Hardness and Wear Resistance: Its high Mohs hardness allows for long-term use under conditions of high friction and high-velocity gas flow impact, reducing nozzle wear.
● Excellent Heat Resistance: With a high melting point, it maintains structural stability and orifice precision even in high-temperature environments.
● High Chemical Inertness: Highly resistant to corrosion by acids, alkalis, and many corrosive gases, reducing the risk of deposition and workpiece contamination.
● Low Thermal Expansion Coefficient: Maintains dimensional stability even against rapid temperature changes.
● Processing Flexibility: Capable of being machined into complex shapes and supports customization of orifice diameters. Overall performance can be improved by combining with composite materials.
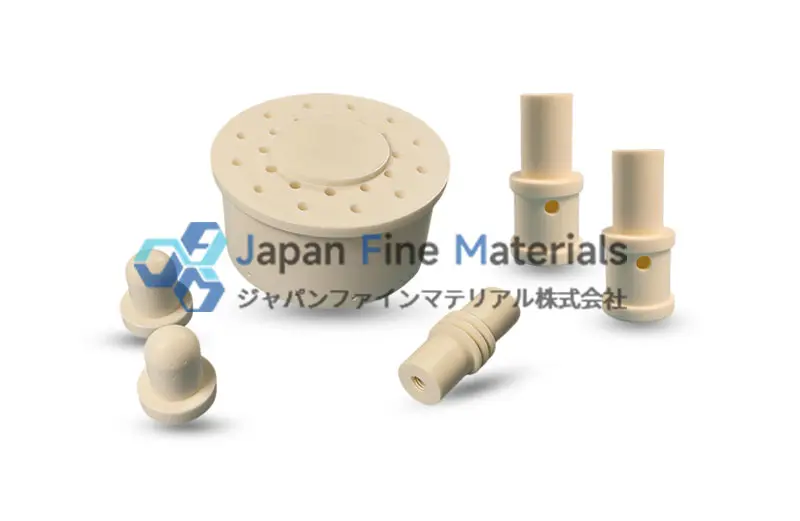

2. Aluminum Nitride (AlN) Ceramic Nozzles
Aluminum Nitride (AlN) is a high-performance ceramic material widely used in plasma etching equipment and microelectronics processing. It not only possesses excellent thermal conductivity and mechanical strength but also maintains dimensional stability and chemical inertness in high-temperature, frequent thermal-cycling environments. This makes it suitable for applications requiring strict processing precision and equipment reliability. Furthermore, AlN has good electrical insulation properties, helping to suppress static electricity buildup in microelectronics manufacturing and protecting both the workpiece and the equipment.
● High Thermal Conductivity: Quickly dissipates heat, reducing localized overheating and improving process stability.
● High Thermal Shock Resistance: Resistant to cracking and deformation even under rapid temperature changes, suitable for high-frequency etching cycles.
● High Mechanical Strength: Strong against bending and compression, maintaining structural integrity even in high-pressure or vibrating environments.
● Excellent Electrical Insulation: High dielectric strength (breakdown strength) reduces the influence of static electricity in micro-processing, lowering the risk of damage to the wafer.
● High Dimensional Stability: Low thermal expansion coefficient maintains micron-level micro-hole precision even under fluctuations in temperature and pressure.

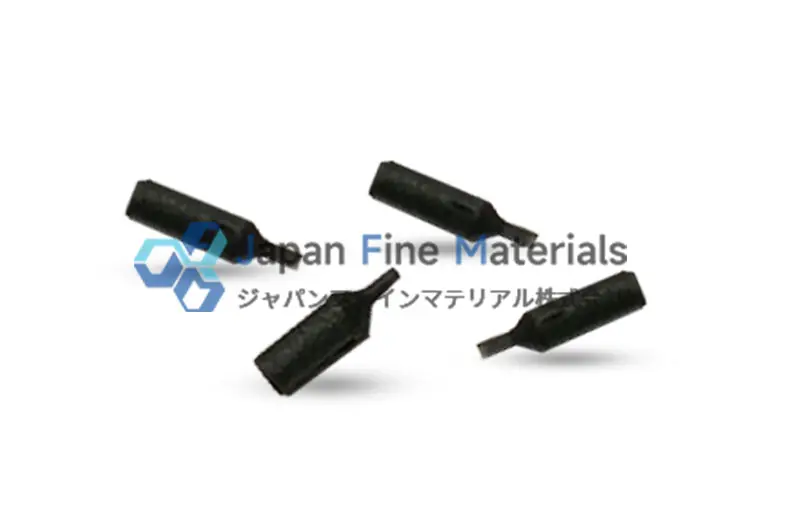
3. Zirconia (ZrO₂) Ceramic Suction Nozzles
Zirconia (ZrO₂) is a high-performance ceramic material widely adopted in high-end plasma etching equipment for semiconductor manufacturing and precision microelectronics processing due to its excellent fracture toughness and thermal cycle stability. ZrO₂ can withstand high mechanical stress and high-temperature/corrosive environments while maintaining dimensional accuracy and structural integrity, making it suitable for applications with extremely demanding process precision and equipment reliability. Furthermore, zirconia stabilized with Yttria (Y₂O₃) optimizes thermal expansion characteristics, enabling long-term stable operation even in environments with frequent operating cycles or large temperature fluctuations.
● Excellent Fracture Toughness: High fracture toughness allows it to withstand high-pressure gas flow impacts and mechanical vibrations, reducing the risk of nozzle breakage.
● High Chemical Stability: Maintains properties even in corrosive gas/liquid environments and is less susceptible to chemical erosion (etching).
● High Mechanical Strength: Maintains structural integrity and dimensional stability even in high-stress environments.
● High-Precision Machinability: Can be machined into complex shapes, suitable for customized orifice diameters and high-precision applications.
● High Wear Resistance: High-hardness material suppresses the propagation of micro-cracks, promising a longer lifespan than general ceramic suction nozzles.
● Excellent Corrosion Resistance: Exhibits high chemical stability against some organic solvents, cleaning agents, acid/alkali solutions, and corrosive gases. It is resistant to particle precipitation and corrosion even under long-term chemical contact, contributing to the maintenance of dimensional accuracy.

Alumina (Al₂O₃) vs. Aluminum Nitride (AlN) vs. Zirconia (ZrO₂)
|
Properties |
Alumina (Al₂O₃) |
Aluminum Nitride (AlN) |
Zirconia (ZrO₂) |
|
Thermal Conductivity |
Low |
Extremely High |
Low |
|
Hardness / Wear Resistance |
High |
Moderate |
Extremely High |
|
Thermal Shock Resistance |
Average |
Excellent |
Excellent |
|
Fracture Toughness |
Low |
Low |
High (Tough) |
|
Cost |
Low |
High |
Medium to High |
|
Typical Applications |
Semiconductor etching, precision spraying, substrate handling jigs |
Precision microelectronics processing, MEMS etching, and high-power heat dissipation |
SMT precision component transport, chip pick-and-place (mounting) |
● Alumina (Al₂O₃): Excellent wear resistance and relatively low cost make it suitable for many industrial applications such as semiconductor etching, precision spraying, and substrate transport jigs. However, its thermal shock resistance in environments with rapid temperature changes is only average.
● Aluminum Nitride (AlN): Characterized by extremely high thermal conductivity and excellent thermal shock resistance, it is suitable for high-precision microelectronics processing, MEMS etching, and high-power heat dissipation. However, the material is brittle, the cost is high, and the processing difficulty tends to be greater.
● Zirconia (ZrO₂): With very high fracture toughness and hardness, it can withstand mechanical impacts and vibrations during high-speed operation, making it ideal for SMT precision component transport and chip pick-and-place. However, due to its low thermal conductivity, attention must be paid to heat accumulation (temperature rise).
Material Selection Guide
1. Operating Temperature and Thermal Shock Resistance
Ceramic nozzle materials must withstand the high temperatures generated in plasma etching and high-precision processing, maintaining structural integrity and mechanical properties even during long-term exposure. In high-frequency plasma etching or in conditions involving rapid heating and cooling, thermal shock resistance is particularly important to prevent cracking and breakage, enabling long-term, stable use. Additionally, prolonged high-temperature operation can alter the microstructure, potentially affecting orifice precision.
For this reason, Aluminum Nitride (AlN) and Zirconia (ZrO₂) are preferred for high-temperature environments with significant thermal shock, while Alumina (Al₂O₃) is suitable for medium-to-high temperature processes with stable conditions.
2. Chemical Compatibility and Corrosion Resistance
Nozzle materials are required to have high chemical stability against the gases, plasma, and chemicals used in the process, reducing the risk of surface corrosion, flow path blockage, and particle shedding to ensure process reproducibility. Surface roughness (finish) and microstructure density are effective in suppressing deposit adhesion and improving durability.
In strongly corrosive gas environments, high-purity Alumina (Al₂O₃) and Zirconia (ZrO₂) generally exhibit more stable chemical properties and are strong candidates.
3. Mechanical Strength and Wear Resistance
Since ceramic nozzles are used in environments with high-velocity gas flows, fine-particle collisions, and mechanical vibrations, they require sufficient compressive, flexural, and wear-resistant properties. For precision parts, material uniformity and density are the foundation for maintaining dimensional accuracy.
In high-frequency or continuous operation conditions, selecting high-toughness ceramics (e.g., stabilized zirconia) can significantly extend service life. Therefore, for applications with high mechanical stress and susceptibility to wear, Zirconia (ZrO₂) and high-strength Alumina (Al₂O₃) are recommended.
4. Precision and Dimensional Stability
In microelectronics processing and semiconductor etching, nozzle orifice precision is required at the micron level. It is important to appropriately manage the material's thermal expansion coefficient and internal stress to ensure long-term stability. Furthermore, molding processes for complex orifice shapes or multi-hole nozzles (such as injection molding or cold isostatic pressing) also affect dimensional reproducibility.
For high-precision applications, Aluminum Nitride (AlN) offers excellent dimensional stability with low thermal expansion, and Zirconia (ZrO₂) is also suitable for precision use due to its high thermal shock resistance. Alumina (Al₂O₃) is widely used in mainstream precision processing and can meet most dimensional accuracy requirements.
5. Cost-Performance and Lifespan
While high-performance ceramics have a relatively high initial cost, their wear and corrosion resistance help reduce the frequency of maintenance and replacement. In mass production and high-precision processes, long-term reliability and process stability should be prioritized over simple low-cost orientation.
In terms of balancing cost and performance, Alumina (Al₂O₃) is suitable for moderate requirements, while Aluminum Nitride (AlN) and Zirconia (ZrO₂) are appropriate for high-end precision processes.
6. Process Compatibility
Requirements for nozzle orifice shape, wall thickness, and thermal conductivity vary for each etching process. Material selection must align with the equipment's process conditions to ensure uniform gas distribution, stable etching rates, and suppression of localized over-etching or deposition-induced blockages.
For processes requiring high uniformity, high thermal conductivity, and high stability, Aluminum Nitride (AlN) is the first choice, while Alumina (Al₂O₃) and Zirconia (ZrO₂) can be selected flexibly based on process temperature or wear resistance requirements.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate ceramic nozzle material is essential for achieving long-term stable operation of plasma etching equipment, ensuring micron-level processing precision, and improving product yield. By scientifically understanding material properties, process requirements, and the actual operating environment, and combining them with an appropriate selection strategy, one can extend the lifespan of ceramic nozzles while reducing equipment maintenance costs and production risks. Furthermore, high-quality ceramic nozzles optimize gas flow distribution and ensure etching reproducibility and consistency, strongly supporting microelectronics manufacturing, semiconductor processing, and precision industrial applications.
Are you having trouble selecting nozzles for your plasma etching equipment? If you are looking for high-performance ceramic nozzles that suit your operating conditions, please contact JFM. We provide professional custom solutions covering everything from material selection to precision machining, supporting stable operation even under high-temperature, highly corrosive, and high-precision processes. We help improve your production efficiency, yield, and equipment reliability.