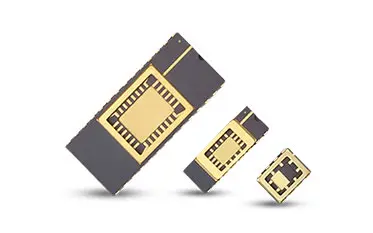
Custom Alumina Ceramic Components for Semiconductor Applications
Custom Alumina components for semiconductor tools. High-purity Al2O3 offers superior plasma resistance and thermal stability for wafer handling and etching.
What are ceramic packages in semiconductor applications?
Ceramic packages ensure electrical and thermal stability for chips. Using Alumina, AlN, and Si3N4, they offer heat resistance and reliability for power and RF devices.
Ceramic Components in Semiconductor Etching Equipment
Discover how selecting the right precision ceramic materials for etching components optimizes semiconductor process stability and maximizes wafer yield.
How Alumina Ceramics Are Made: Process, Features, and Uses
This comprehensive guide details the manufacturing process, key features, and industrial applications of Alumina Ceramics, emphasizing how precise process control ensures reliability in semiconductor and precision machinery sectors.
What are Porous Ceramics: Characteristics and Industrial Advantages
Porous ceramics combine a controlled microstructure with strength and stability. Essential for filtration and semiconductors, they balance porosity and durability for modern precision engineering and high-performance components.
Why Choose Custom Porous Ceramics for Advanced Industrial Applications?
Custom porous ceramics deliver superior strength and reliability through optimized pore structures. Ideal for semiconductor and thermal applications, they maximize process efficiency compared to standard products.
Why Ceramic Nozzles are Essential for Semiconductor Plasma Etching Equipment
High-purity ceramic nozzles stabilize gas flow and plasma distribution in semiconductor etching. Their superior heat and corrosion resistance minimize contamination, extend component life, and boost wafer yields while reducing maintenance costs.
Semiconductor Ceramic Nozzles :Material Types and Selection Guide
A technical guide to ceramic nozzle materials for plasma etching. Learn to select the right Alumina, AlN, or ZrO₂ components to enhance precision, durability, and production yield in microelectronics manufacturing.
How Ceramic Chambers and Domes Enhance Semiconductor Manufacturing Yield
Ceramic chambers and domes resist extreme heat and plasma to ensure process stability. Their thermal uniformity and corrosion resistance minimize contamination, directly boosting film quality and manufacturing yield.